Unmasking the Mystery: Why Do I Snore?
Snoring is a common nighttime issue that can be quite bothersome for both the snorer and their sleeping partners. Just ask my wife.
What Causes Me to Snore?
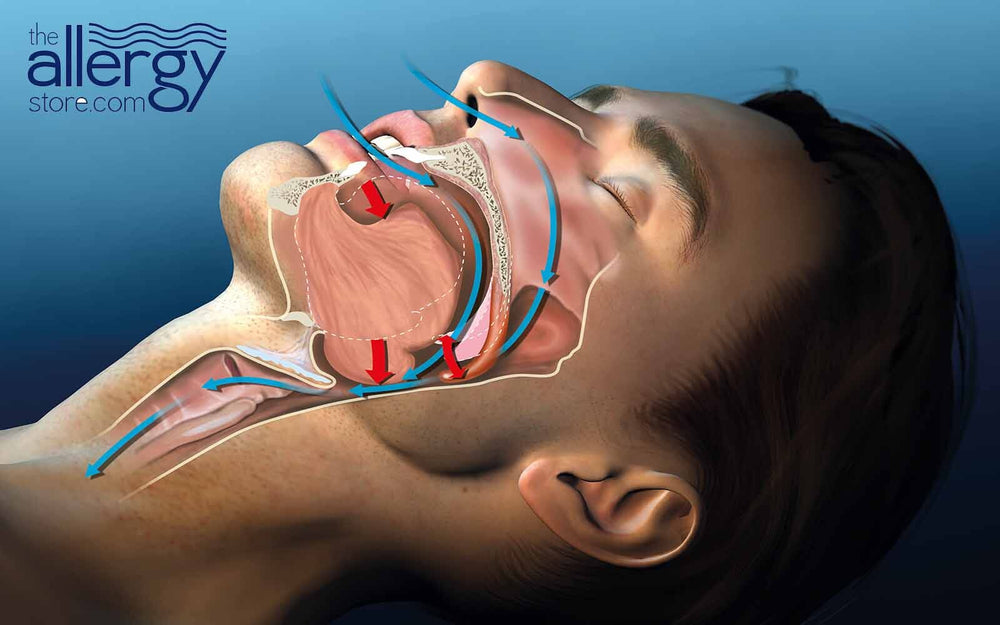
Snoring can occur when the flow of air through the mouth and throat is partially blocked during sleep. But what exactly causes this obstruction and the all-too-familiar sound of snores? It turns out, there are several factors at play.
- One culprit is the relaxation of throat muscles during sleep. For some, this can lead to a narrowing of the airway, causing turbulence and the not-so-soothing sound of snoring.
- But that's not all. Nasal congestion from allergies, colds, or structural issues can also contribute to snoring. When it's difficult to breathe through the nose, people may resort to breathing through their mouths, increasing their chances of snoring.
- And let's not forget about the impact of alcohol and sedatives. While they may help us relax, they can also relax the muscles in our throat, setting the stage for snoring.
- Your sleep position may also play a role. Sleeping on your back can cause your tongue and soft palate to collapse to the back of your throat, blocking airflow and leading to snoring. So, switching to your side may help reduce the snore factor.
- But age and genetics can also have a say in the matter. Snoring can be influenced by genetic factors and may become more common as we age due to changes in muscle tone and tissue laxity.
- It's important to note that snoring can also be a symptom of a more serious condition called sleep apnea. According to Cleveland Clinic "Sleep apnea is a disorder that causes you to stop breathing while asleep. Your brain tries to protect you by waking you up enough to breathe, but this prevents restful, healthy sleep. Over time, this condition can cause serious complications" If your snoring is accompanied by loud, frequent gasping or choking sounds, it may be a red flag for sleep apnea and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
While many factors contribute to snoring, one lesser-known factor that may be surprising to some.
You may be surprised to learn that the little critters living in your bedroom, dust mites, could be the culprit.
- These sneaky allergens from dust mites can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals, causing inflammation in the nose and throat. This can lead to breathing difficulties during sleep and, you guessed it, snoring.
- And that's not all - dust mite allergens can also congest the nasal passages, making mouth breathing more likely and snoring more common.
- To make matters worse, these pesky allergens can even boost mucous production, further obstructing your airways and increasing your chances of snoring.
Even if you don't have allergies, the allergens produced by dust mites can make snoring worse. So next time you drift off to sleep, remember that there are tiny critters sleeping with you too.
Time to kick those dust mites out of your bedroom!
How Do I Stop Snoring?
Do you find yourself tossing and turning in bed because of your annoying snores? Take control of your sleep by trying out these simple yet effective techniques to reduce or eliminate snoring:
- Shed Those Unwanted Pounds: NLM Studies show carrying extra weight, especially around your neck, can be the culprit behind your snoring.
- Switch Up Your Sleeping Position: Did you know that sleeping on your back can increase your chances of snoring? Change up your sleep position and opt for snoozing on your side to keep your airways clear. You can even use innovative pillows or tools to help you maintain a side sleeping position.
- Put a Limit on Alcohol and Sedatives: That evening glass of wine may seem tempting, but it can do a number on your snoring. Avoid alcohol and sedatives before hitting the sack, as they relax the throat muscles and lead to more snoring.
- Fight Allergens: Dust mites can be a major annoyance for those prone to snoring. Take proactive measures to reduce your exposure like using allergen-proof bedding, washing your sheets regularly, and investing in a trustworthy air purifier with a HEPA filter for your bedroom.
- Keep Hydrated: When it comes to reducing snoring, hydration is key. Keep your throat lubricated by staying hydrated throughout the day with plenty of water.
- Nasal Strips or Dilators: Decongest and breathe easy with the help of over-the-counter nasal strips or dilators. These tiny and inexpensive products open up your nasal passages, making it easier to breathe through your nose and stop snoring.
- Find Relief with Oral Appliances: Dentists are eager to help you say goodbye to snoring by fitting you with customized oral appliances that reposition your jaw and tongue to keep your airway open while you sleep. These devices are especially effective for those with mild to moderate sleep apnea.
Seek Professional Help: If snoring persists even after trying these tips, don't hesitate to consult with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist. They can identify any underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatments like CPAP therapy or even surgery in severe cases.
So, don't suffer any longer, get help and snooze soundly without snoring.
Can Snoring Be a Sign of a More Serious Problem?
Yes, snoring can sometimes be a sign of a more serious underlying health issue, particularly when it is associated with other symptoms or risk factors.
The most notable condition linked to snoring is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). OSA is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of partial or complete blockage of the upper airway during sleep.
Key points about OSA and its association with snoring:
-
Loud and Persistent Snoring: People with OSA often snore loudly and persistently throughout the night. The snoring may be accompanied by pauses in breathing.
-
Daytime Fatigue: Individuals with OSA frequently experience daytime fatigue, excessive sleepiness, and difficulty concentrating due to disrupted sleep patterns.
-
Increased Health Risks: Untreated OSA is associated with an increased risk of serious health problems, including hypertension, heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and obesity.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosis of OSA typically involves a sleep study conducted by a sleep specialist. Treatment options may include lifestyle changes, CPAP therapy, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
It's important to recognize that not all snoring is indicative of sleep apnea, but persistent and loud snoring, especially when accompanied by other symptoms, should not be ignored.
Talking to you doctor or sleep specialist for a proper evaluation is crucial in identifying and addressing any underlying sleep disorders or health concerns.
Till next time!

